Unveiling the Role of Flavoring Agents in Pharmaceuticals
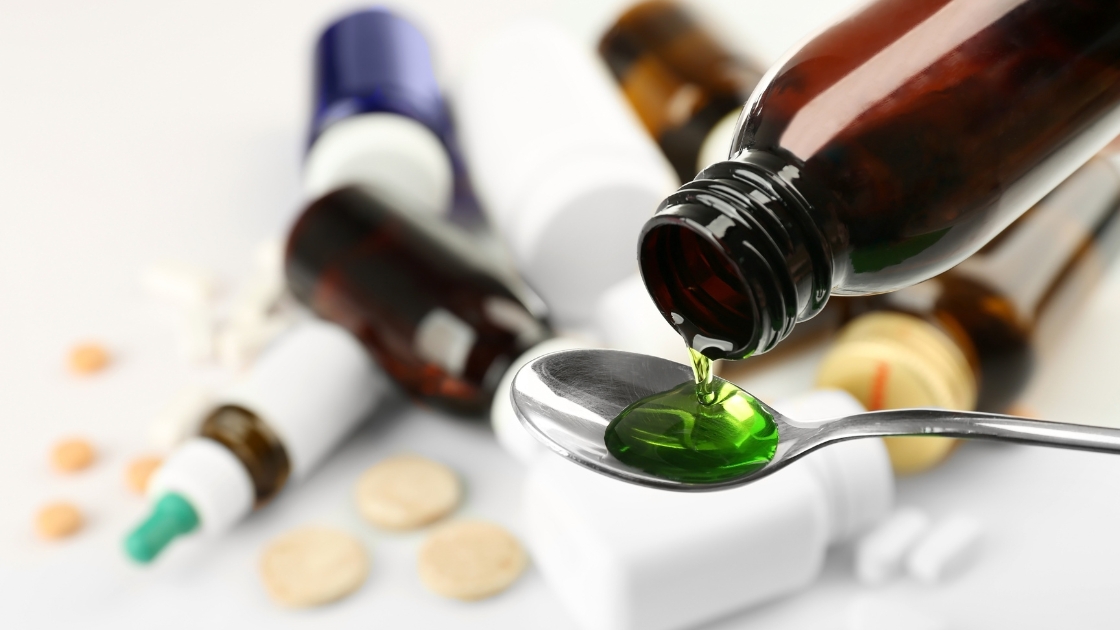
In this enlightening blog, readers can expect to delve into the fascinating world of flavouring agents in pharmaceuticals. Unveiling their vital role, the article will explore how these agents enhance the palatability of medicines, especially for children and elderly patients, aiding in compliance and better treatment outcomes. Readers will gain valuable insights into the science behind flavour selection, potential challenges, and the future outlook of this essential aspect of pharmaceutical formulation. Whether you are a healthcare professional, researcher, or simply curious, this article promises a comprehensive and engaging exploration.
Role of Flavoring Agents in Pharmaceuticals
Role of flavouring agents in the pharmaceutical industry is very crucial in making medications more palatable and user-friendly. Medicines, especially those administered to children and elderly patients, often have an unpleasant taste or odor, which can lead to non-compliance and treatment discontinuation. Flavouring agents in pharmaceuticals are employed to mask the bitterness, astringency, or overall unpleasant taste of these drugs, making them more appealing and easier to ingest.
One primary advantage of using flavouring agents in pharmaceuticals is their ability to improve patient adherence to prescribed medications. When drugs taste better, patients are more likely to take them as directed, leading to better treatment outcomes. For paediatric patients, who may be particularly sensitive to the taste of medicines, flavoured formulations can reduce resistance and fear associated with taking medication.
Moreover, flavouring agents in pharmaceuticals can enhance the overall patient experience, fostering a positive association with medication usage. This is especially beneficial for patients with chronic conditions who require long-term drug therapy. It can lead to increased patient satisfaction and a higher quality of life.
However, while flavouring agents in pharmaceuticals offer numerous advantages, their selection must be done carefully, considering potential interactions with the active ingredients and ensuring they comply with regulatory guidelines.
The role of flavouring agents in pharmaceuticals is indispensable in making medicines more palatable, improving patient adherence, and ultimately enhancing treatment outcomes. By addressing the taste-related challenges of medications, flavouring agents in pharmaceuticals contribute to the overall effectiveness and patient satisfaction in the realm of pharmaceutical formulations.
Natural Flavouring Agents vs Artificial Flavouring Agents in the Pharmaceutical Industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, both natural and artificial flavouring agents are used to improve the taste and palatability of medications. Each type of flavouring agent has its own set of advantages and considerations.
Natural Flavouring Agents in Pharmaceutical Industry
Natural flavouring agents are derived from natural sources such as fruits, herbs, spices, and other plant-based materials. They are often perceived as more desirable by consumers due to their origin from natural sources. These agents can provide a more authentic and familiar taste, making them an appealing choice for pharmaceutical formulations, especially for pediatric and geriatric patients. Natural flavours are generally regarded as safe (GRAS) by regulatory authorities, adding to their appeal in the pharmaceutical industry.
Artificial Flavouring Agents in Pharmaceutical Industry
Artificial flavouring agents, also known as synthetic or chemical flavours, are manufactured in a laboratory using various chemical processes. These agents offer a wide range of flavors that may not be readily available in nature, allowing for greater flexibility and consistency in formulation. They can be more cost-effective than natural flavours and often provide stronger and more intense flavors. However, there may be concerns about the safety and potential long-term effects of certain artificial flavouring agents, leading to regulatory scrutiny and limitations on their use.
Balancing Factors:
The choice between natural and artificial flavouring agents in the pharmaceutical industry involves careful consideration of several factors. These include taste, cost, availability, safety, and regulatory compliance. Pharmaceutical companies must weigh the benefits of using natural flavours to appeal to health-conscious consumers and those seeking familiar tastes, against the advantages of artificial flavours in providing unique and consistent flavor profiles.
Ultimately, the goal of both types of flavouring agents is to enhance patient compliance and overall treatment effectiveness by improving the palatability of medications. Striking the right balance between natural and artificial flavouring agents ensures that pharmaceutical formulations cater to patient preferences while meeting safety and regulatory standards.
Most Used Flavouring Agents in Pharmaceutical Formulations
In pharmaceutical formulations, several flavouring agents are commonly used to enhance the palatability of medications and improve patient compliance. The choice of flavouring agents depends on the type of drug, the target patient population, and regulatory considerations. Some of the most widely used flavouring agents in pharmaceutical industry include:
- Fruit Flavors: Natural fruit flavours such as strawberry, orange, cherry, and banana are popular choices for masking the bitterness of medications. They are especially common in paediatric formulations.
- Mint Flavors: Peppermint and spearmint are commonly used to provide a refreshing and cooling sensation, making them suitable for cough drops, lozenges, and oral care products.
- Vanilla: Vanilla is a versatile flavour that compliments a wide range of medications, including liquid formulations and chewable tablets.
- Citrus Flavors: Lemon, lime, and citrus blends are often used to add a zesty and tangy taste to various medications.
- Bubblegum: Bubblegum flavour is favoured in paediatric formulations and chewable medications, making them more enjoyable for children.
- Chocolate: Chocolate flavouring is used in chewable tablets and oral suspensions, providing a familiar and pleasant taste.
- Berry Flavors: Raspberry, blueberry, and mixed berry flavours are commonly used in various pharmaceutical formulations.
- Caramel: Caramel flavour adds a sweet and slightly toasted taste to medications, improving their overall palatability.
- Cinnamon: Cinnamon flavour is used to mask the bitter taste of some drugs while adding a warm and spicy note.
- Anise: Anise flavour is often used in cough syrups and expectorants due to its soothing properties.
It is essential for pharmaceutical companies to ensure that the flavouring agents used are safe, compliant with regulatory guidelines, and do not interact with the medication's active ingredients negatively. Additionally, they must consider the preferences and needs of the target patient population to create formulations that are both effective and palatable.
Role of Bitter Masking Flavours in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Bitter masking flavours play a critical role in the pharmaceutical industry by addressing one of the most common challenges faced during medication formulation: the bitter taste of certain drugs. Many medications, especially those containing active pharmaceutical ingredients with inherently bitter characteristics, can be highly unpleasant for patients to consume. This bitterness often leads to reduced patient compliance, particularly in paediatric and elderly populations.
Bitter masking flavours are specialised flavouring agents designed to neutralise or cover up the bitter taste of medications without interfering with their efficacy. They work by blocking bitter taste receptors on the tongue or by interacting with the taste buds to create a more palatable experience. By using bitter masking flavours, pharmaceutical companies can significantly improve the acceptability and tolerability of medications, ultimately leading to better patient adherence and treatment outcomes.
The role of bitter masking flavours in the pharmaceutical industry extends beyond merely making medications taste better. They also contribute to enhanced patient experiences, particularly for individuals who may have difficulty swallowing or have heightened sensitivity to bitter tastes. By making medicines more palatable, bitter masking flavours can reduce medication aversion, increase patient satisfaction, and foster a positive association with the treatment process.
In conclusion, the role of flavouring agents in pharmaceuticals is instrumental in enhancing the palatability of medications and improving patient compliance. These agents address the challenge of unpleasant tastes, especially for paediatric and elderly populations, making medications more appealing and easier to ingest. By masking bitterness and other undesirable flavours, flavouring agents contribute to a positive patient experience, fostering better adherence to prescribed treatments. Pharmaceutical companies recognize the significance of selecting appropriate and safe flavouring agents to create patient-friendly formulations. As the industry continues to prioritise patient satisfaction, the role of flavouring agents remains a crucial aspect of optimising medication efficacy and overall patient well-being.
Norex is a renowned flavour manufacturing company that specialises in providing high-quality bitter masking and other flavouring agents in pharmaceutical industry. With a strong commitment to innovation, quality, and customer satisfaction, Norex has established itself as a trusted partner for pharmaceutical companies seeking to improve the taste of their medications.
In addition to bitter masking flavors, Norex offers an extensive portfolio of pharmaceutical flavors, including sweet, fruity, minty, and savory options, catering to a wide variety of medicinal products. Each flavor undergoes rigorous testing and quality control measures to ensure safety, consistency, and compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
Pharmaceutical companies partnering with Norex can benefit from their vast experience, reliability, and dedication to delivering exceptional products and services. Norex's unwavering commitment to providing the best bitter masking and pharmaceutical flavors makes them a preferred choice for companies seeking to enhance the palatability and overall patient experience of their medications.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a flavouring agent in pharmaceuticals?
A flavouring agent in pharmaceuticals is a specialised ingredient used to enhance the taste and palatability of medications. It is added to pharmaceutical formulations to mask bitter or unpleasant tastes, making the medication more appealing and easier to consume, especially for patients who may have difficulty swallowing or are sensitive to the taste of certain drugs. Flavouring agents are crucial in improving patient adherence to prescribed medications, particularly for children and elderly individuals, and play a significant role in creating more patient-friendly pharmaceutical products.
2. What is the use of flavouring agents?
Flavouring agents are used to enhance the taste and palatability of various products, including food, beverages, and pharmaceuticals. In the context of pharmaceuticals, flavouring agents serve the crucial role of masking the bitter or unpleasant taste of medications, making them more appealing and easier to consume for patients. By improving the taste, these agents enhance patient compliance, especially for children and the elderly, who may have difficulty swallowing bitter medications. Flavouring agents play a vital role in creating patient-friendly formulations, ultimately leading to better treatment outcomes and overall patient satisfaction.
3. What are the three types of flavouring agents?
Natural Flavours: Derived from natural sources such as fruits, vegetables, herbs, and spices. These flavours provide an authentic taste and are often perceived as more desirable by consumers due to their natural origin.
Artificial Flavours: Also known as synthetic or chemical flavours, these are manufactured in a laboratory using various chemical processes. They offer a wide range of flavours that may not be readily available in nature and provide greater flexibility in creating unique taste profiles.
Nature-Identical Flavours: These flavours are synthetically produced to mimic natural flavours found in food and beverages. They are chemically identical to the natural flavours but are made in a laboratory setting.












